High-plex immunofluorescence imaging and traditional histology of the same tissue section for discovering image-based biomarkers
Lin JR, Chen YA, Campton D, Cooper J, Coy S, Yapp C, Tefft JB, McCarty E, Ligon KL, Rodig SJ, Reese S, George T, Santagata S, Sorger PK
Nature Cancer (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s43018-023-00576-1
Precision medicine is critically dependent on better methods for diagnosing and staging disease and predicting drug response. Histopathology using Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) stained tissue - not genomics – remains the primary diagnostic method in cancer. Recently developed highly-multiplexed tissue imaging methods promise to enhance research studies and clinical practice with precise, spatially-resolved, single-cell data. Here we describe the “Orion” platform for collecting H&E and high-plex immunofluorescence images from the same cells in a whole-slide format suitable for diagnosis. Using a retrospective cohort of 74 colorectal cancer resections, we show that IF and H&E images provide human experts and machine learning algorithms with complementary information that can be used to generate interpretable, multiplexed image-based models predictive of progression-free survival. Combining models of immune infiltration and tumor-intrinsic features achieves a nearly 20-fold discrimination between rapid and slow (or no) progression, demonstrating the ability of multi-modal tissue imaging to generate high-performance biomarkers.
Publication Access Primary Data Colorectal Cancer Atlas Related Commentary ArticleKey Findings:
-
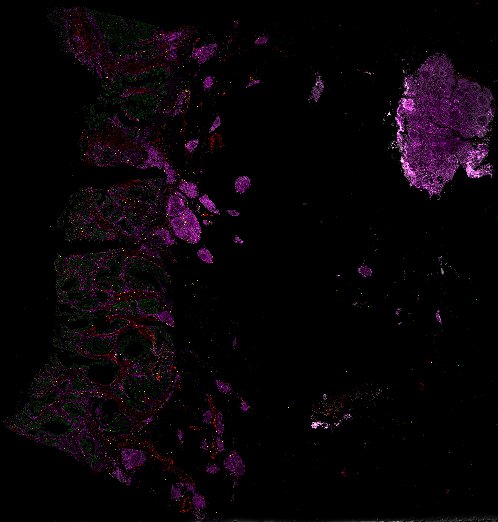
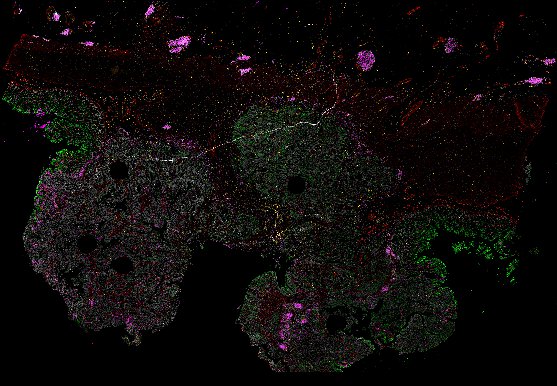
The Orion platform rapidly collects 18-plex immunofluorescence (IF) and diagnostic-grade H&E images from the same cells
-
Complementing H&E with IF (i.e., multimodal imaging) provides greater insight into the molecular features of colorectal cancer samples
-
Machine learning models trained on the multimodal and clinical data predict progression-free survival
-
Analyzing multimodal imaging using machine learning / artificial intelligence methods reveals biomarkers not discoverable by other means
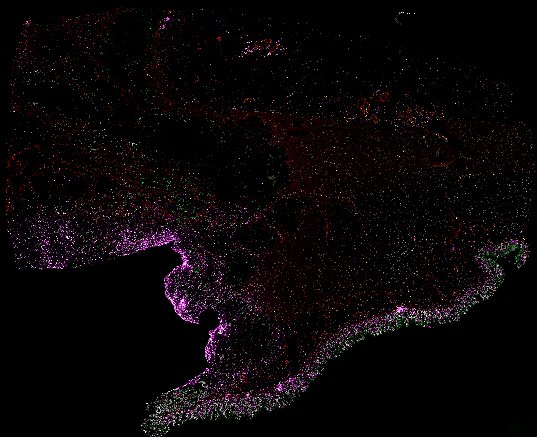
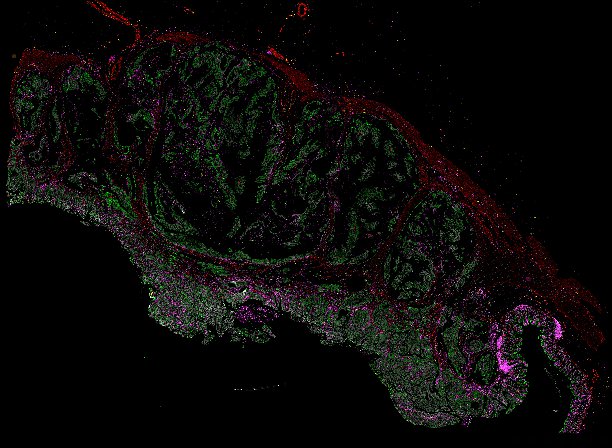
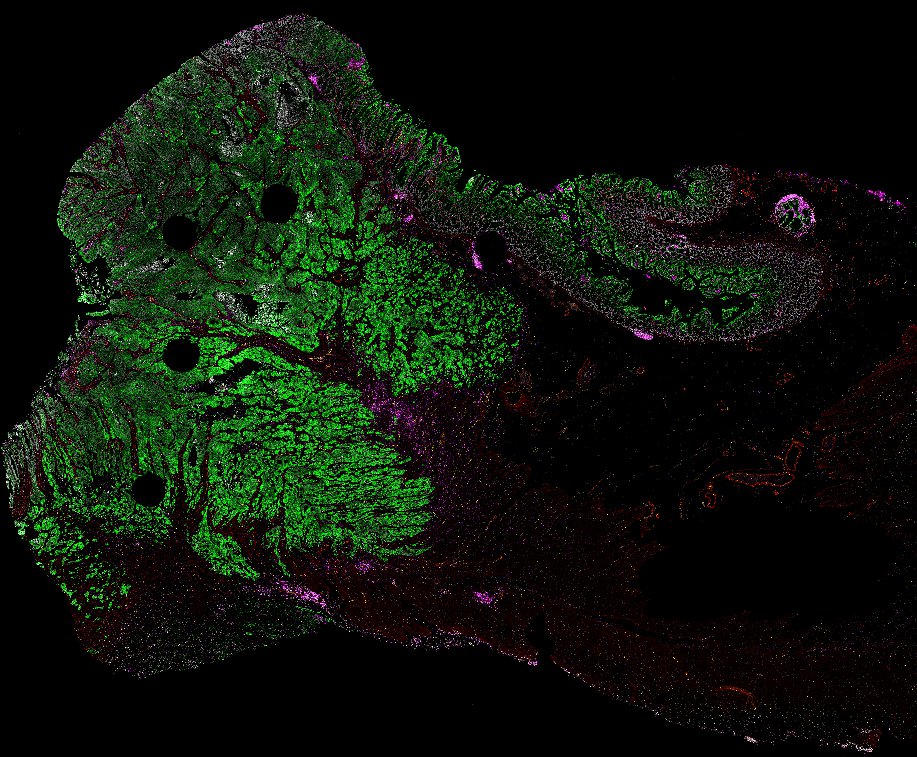
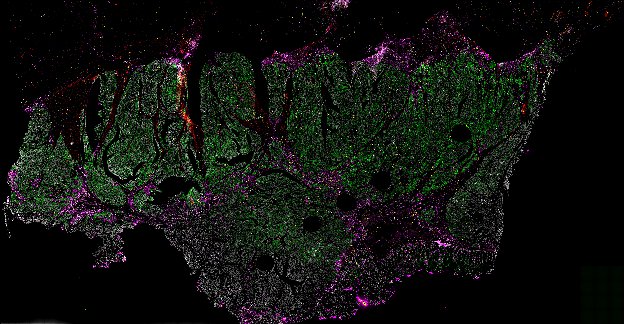
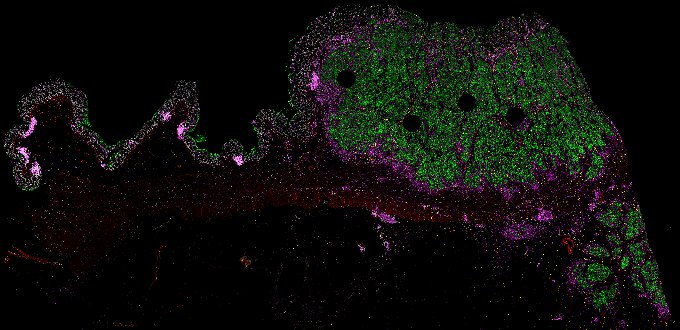
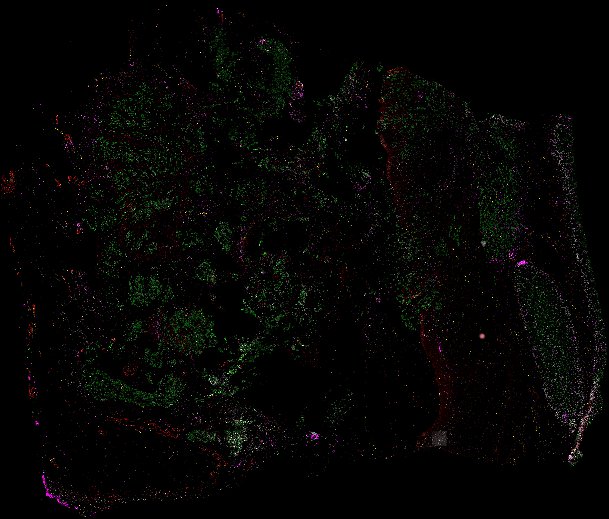
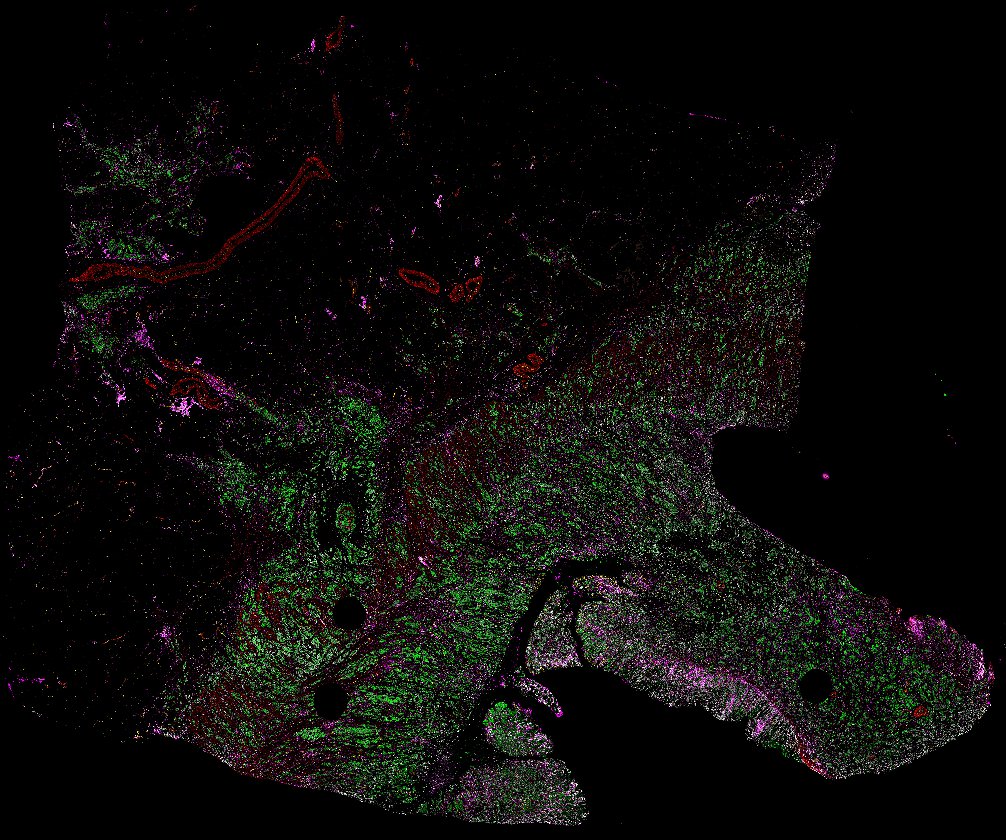
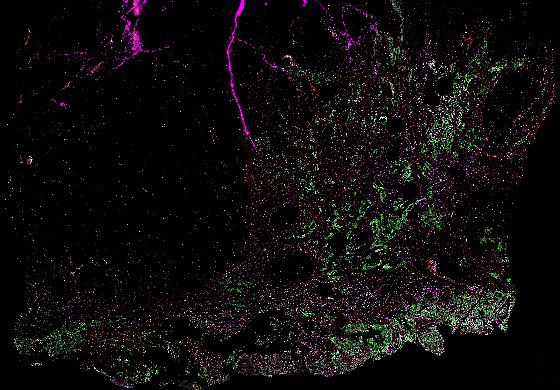
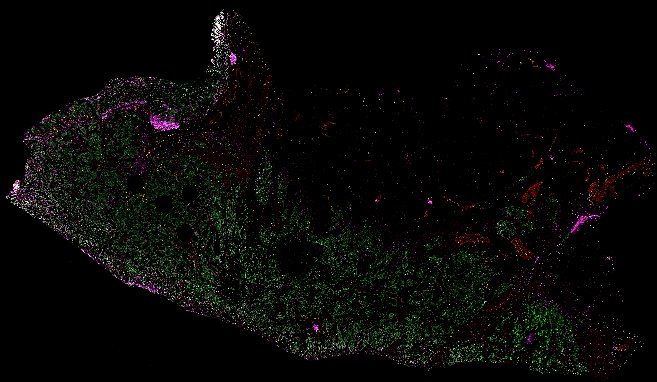
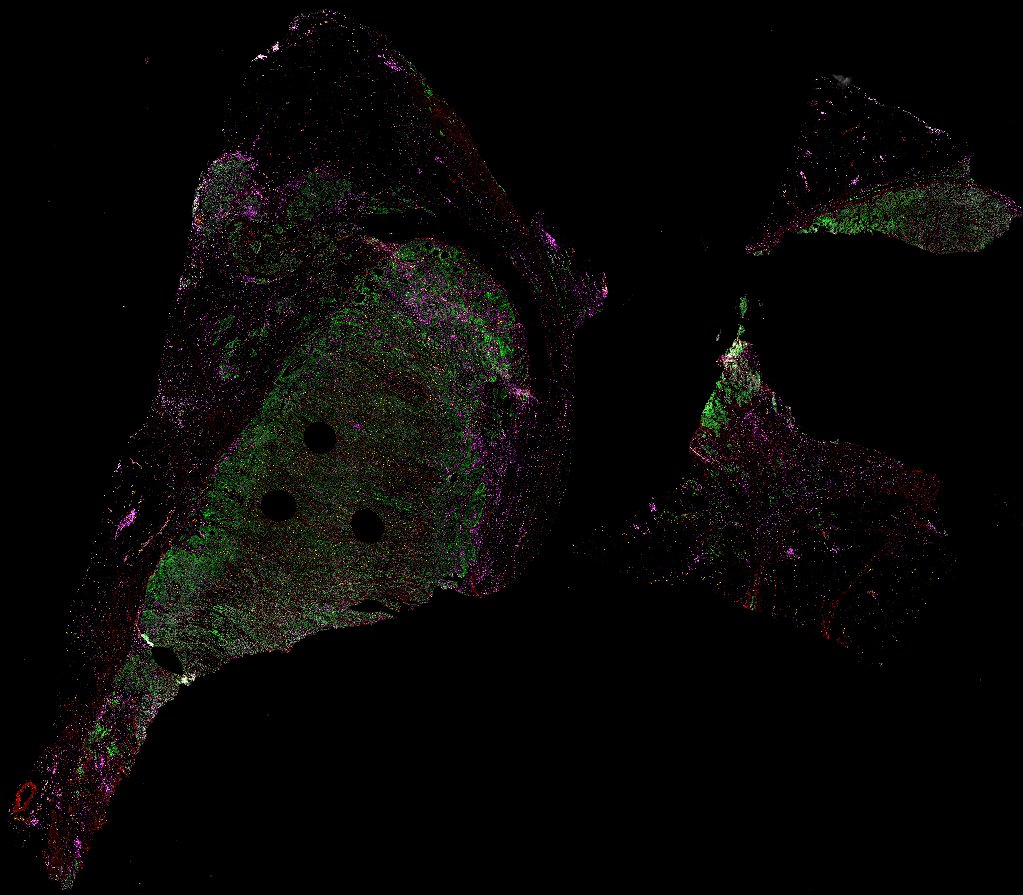
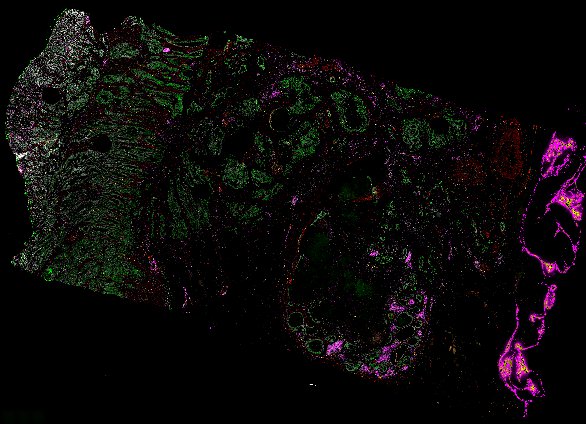
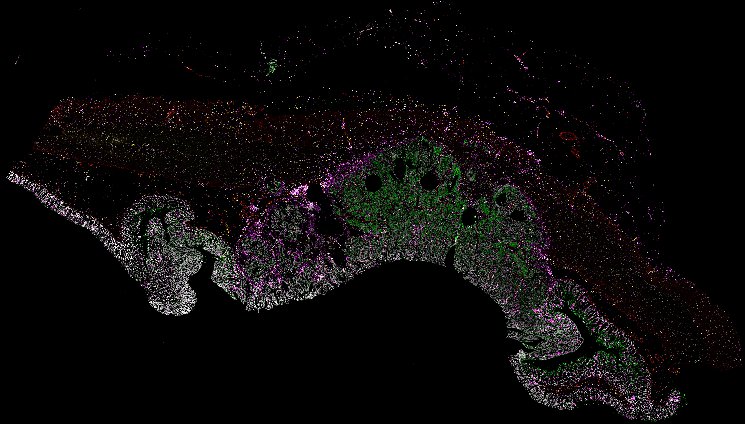
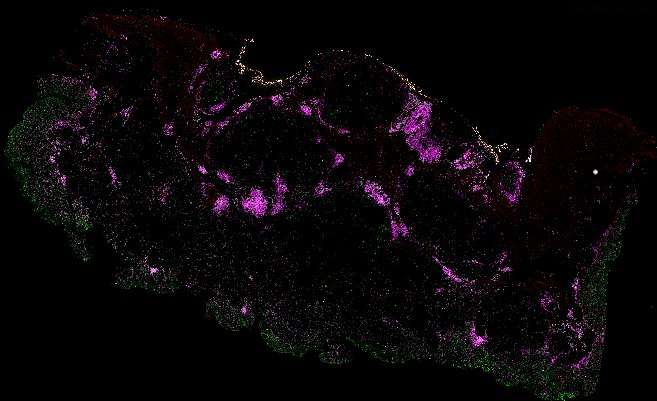
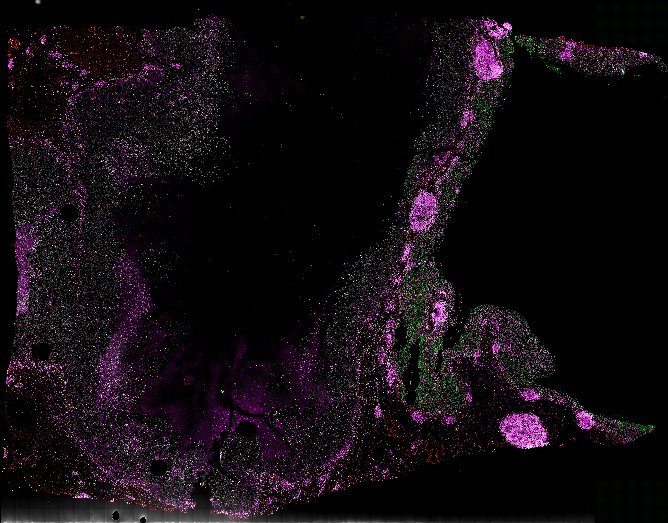
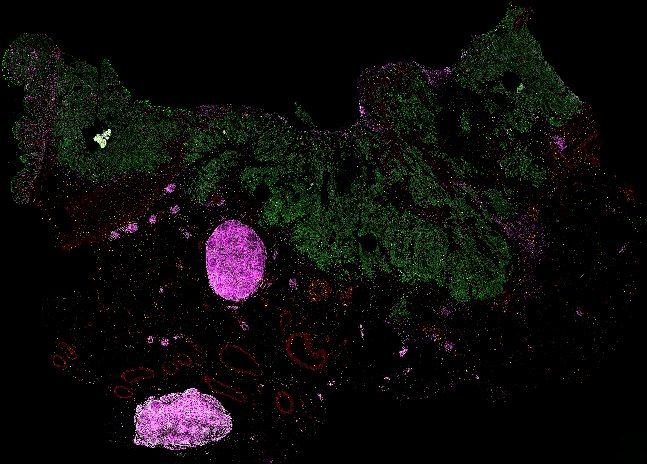
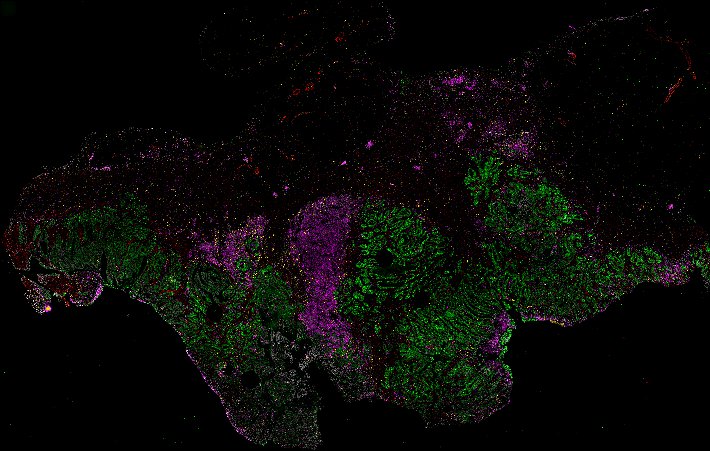
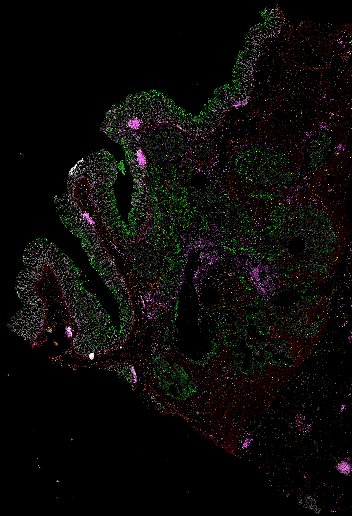
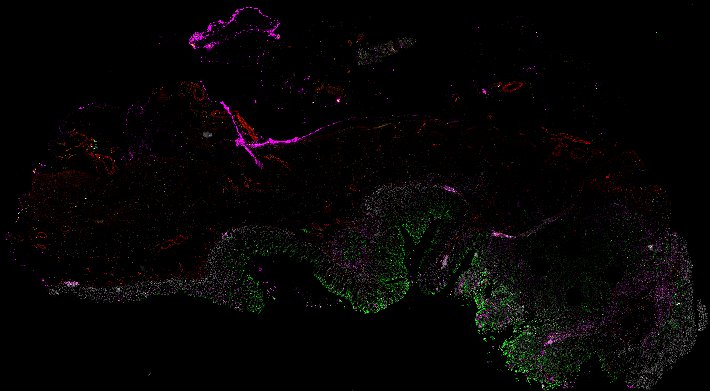
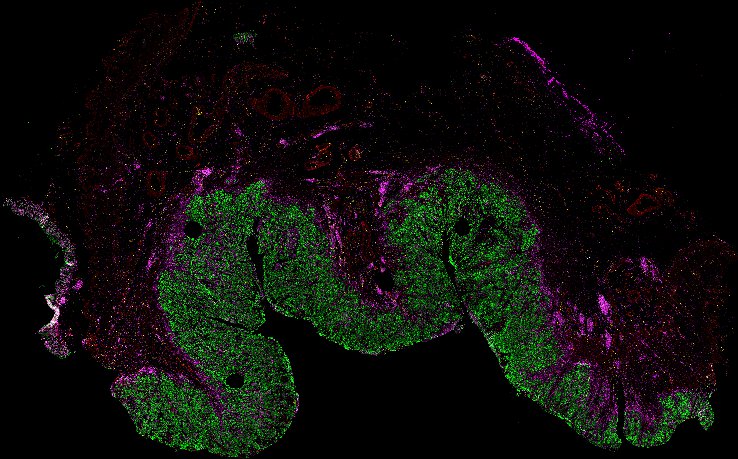
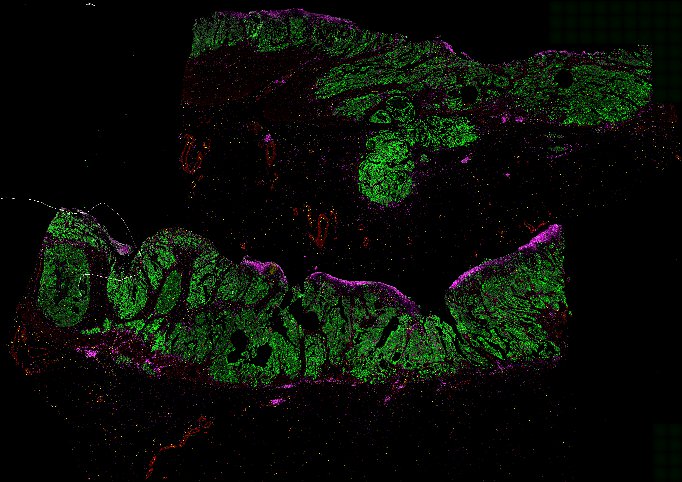
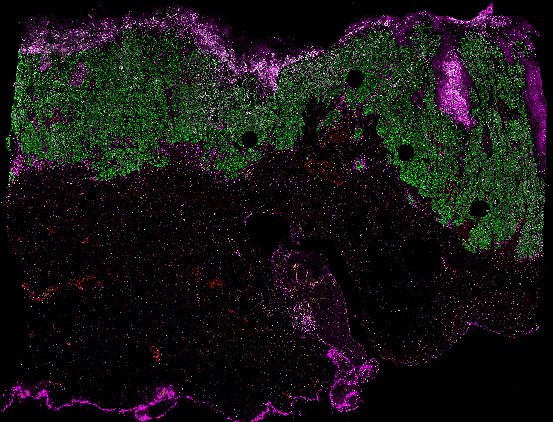
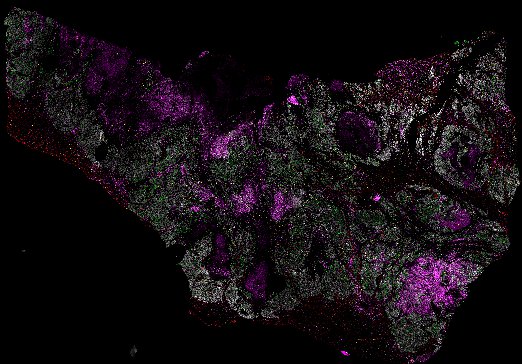
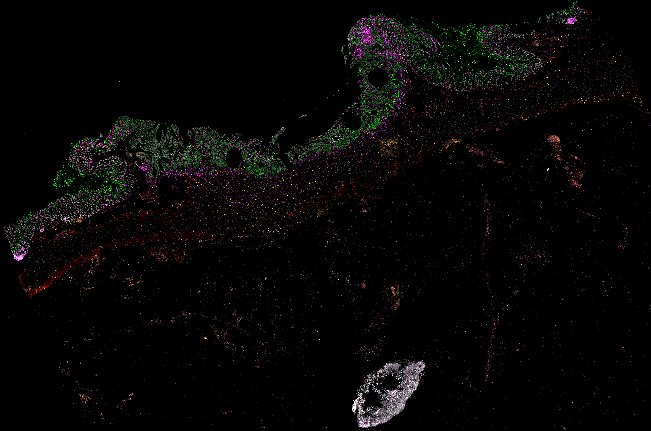
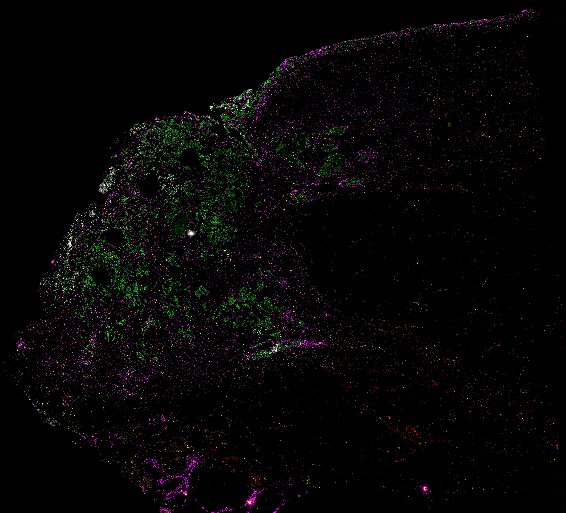
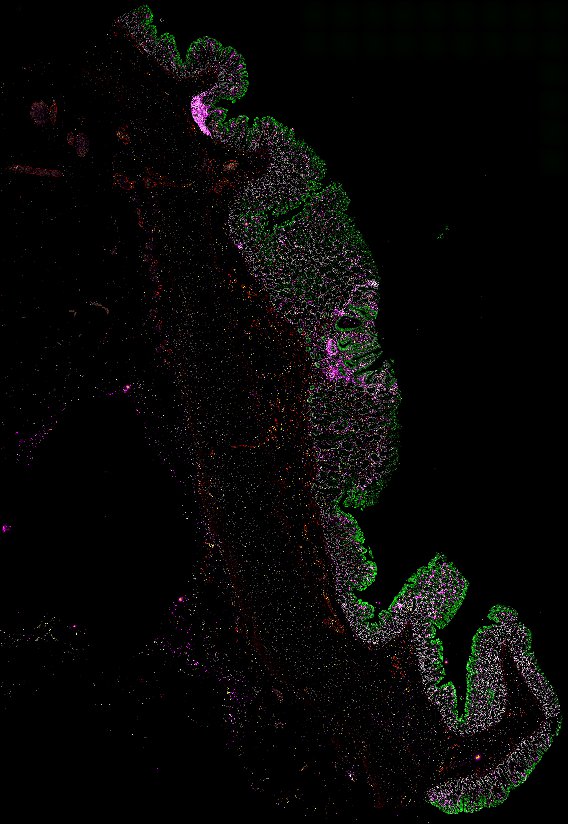
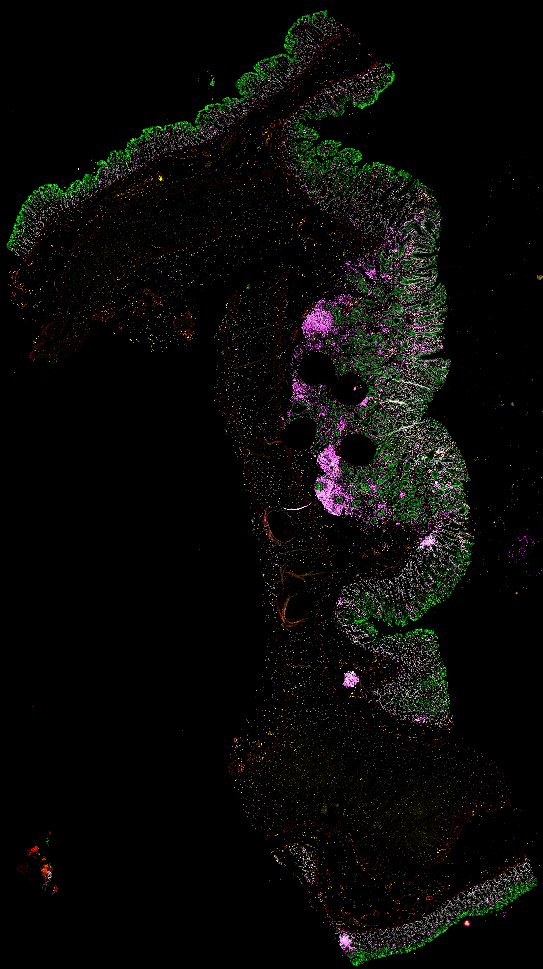
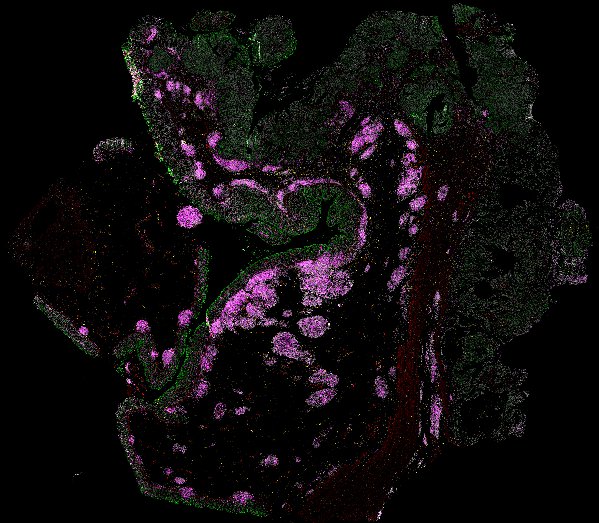
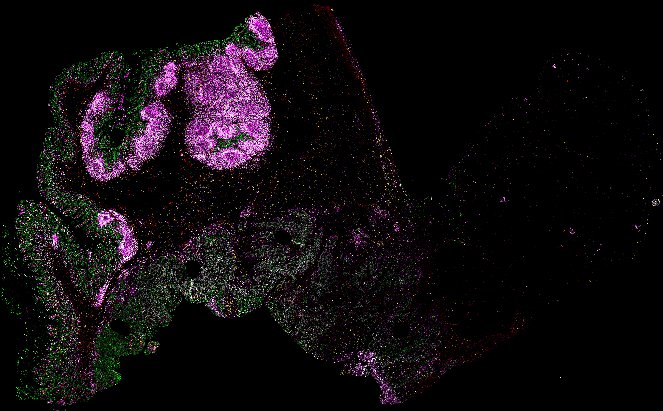
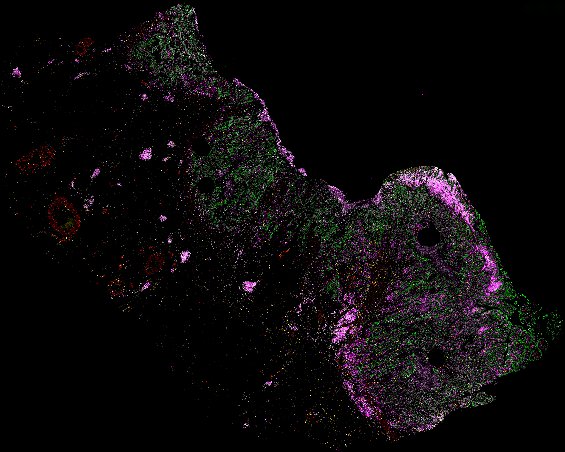
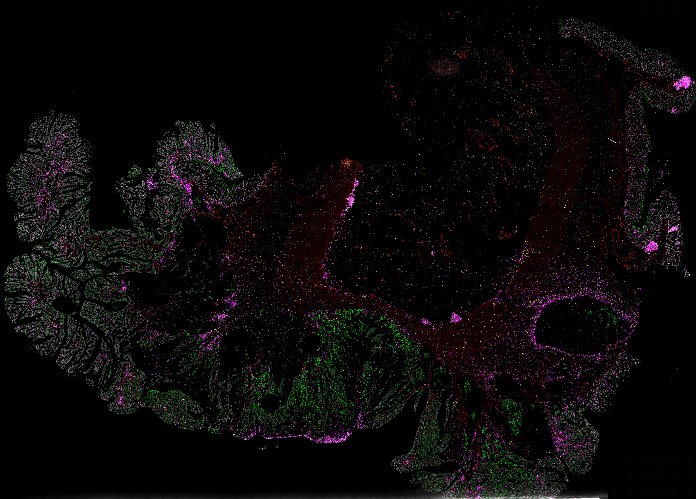
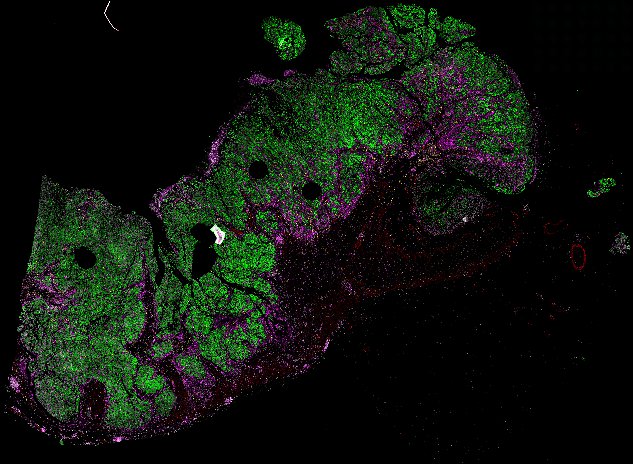
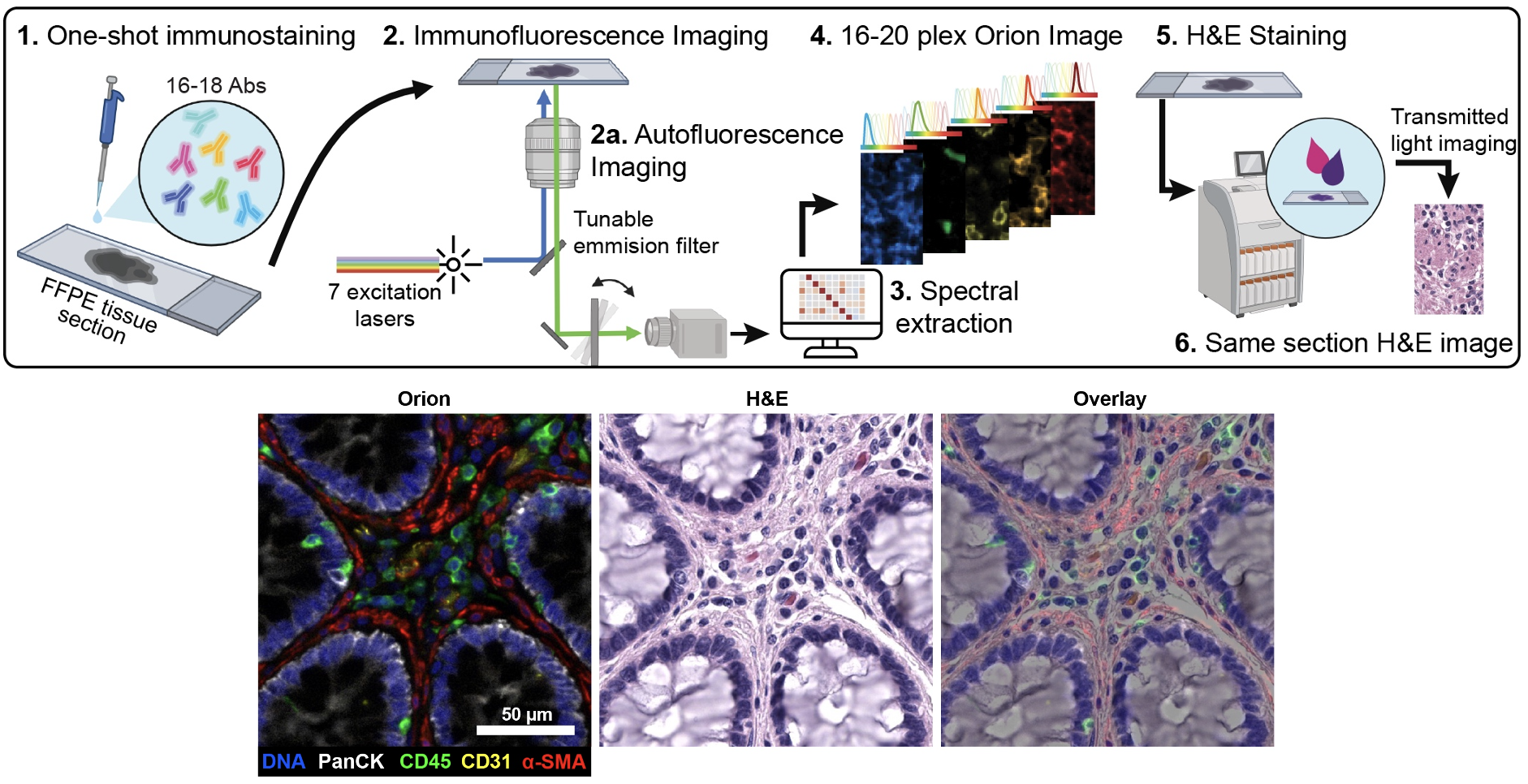
Top: Overview of the Orion method for same-slide immunofluorescence and H&E imaging. Bottom: Example images of a colorectal cancer specimen from Orion, showing the multiplex immunofluorescence image (left; 5 of 18 fluorescence channels shown), the corresponding same-section H&E image (center), and the overlay of these two images (right).
Narrated Minerva Stories
Narrated stories use multi-step narrations and annotations to walk a viewer through key features of the data. Narrated stories distill the multidisciplinary knowledge encompassed by each dataset into a single product that grounds the scientific analyses in the underlying data and metadata. Click the Minerva story icon for an interactive view of the full-resolution images.
Automated Minerva Stories
Automated stories provide basic image viewing with automatic rendering settings, enabling rapid, lightweight sharing of highly multiplexed images, without download. Click the Minerva story icon for an interactive view of the full-resolution images.
Data access
The images in Lin, Chen, Campton et al. (2023) comprise a ~10.5 TB dataset. Visit doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7637655 to view a table detailing where to find each file and data type. This data will eventually also be available via the NCI-sponsored repository for Human Tumor Atlas Network (HTAN; https://humantumoratlas.org).
 Click to enlarge.
Click to enlarge.